Optimize OpenSearch Refresh Interval
This blog post discusses optimizing the refresh interval of an OpenSearch index and how the optimization enhances OpenSearch performance.
Introduction
In OpenSearch, the process of indexing documents initially places them into a memory buffer. At this stage, the documents are not yet searchable. To make these documents searchable, a refresh operation is required. This operation transfers the documents from the memory buffer to new segments. Segments are specific data structures that OpenSearch uses to store and retrieve documents. Once the documents are housed in these segments, they become searchable.
The refresh operation, which enables documents to become searchable by moving them into segments, is managed automatically by OpenSearch. By default, OpenSearch refreshes indexes that have received one or more search requests in the past 30 seconds, every 1 second. This means that documents written to an active index should typically become searchable within 1 second of being written to OpenSearch. While the default refresh frequency for an index is set to 1 second, this setting can be adjusted on a per-index basis.
Why adjust the default index refresh interval
Refresh operations are resource intensive. The procedure of transferring data into new segments and rendering them searchable demands CPU, memory, and input/output (I/O) resources. Consequently, fewer refresh operations can conserve these resources for other tasks.
However, less frequent refreshes also imply a longer wait for newly indexed documents to become searchable. If your use case necessitates near real-time searching of new data, infrequent refreshes may not be appropriate. On the other hand, if your operations can accommodate a delay between the indexing of data and its searching, reducing the frequency of refreshes can liberate resources. This could potentially lead to increased indexing throughput and faster indexing speeds.
View the refresh interval
The frequency of refresh operations is dictated by the refresh interval set for an OpenSearch index. By default, the refresh interval for an index is set to 1 second. This implies that a refresh operation will be executed every second, provided the index is active. An index is considered active if it has received one or more search requests within the last 30 seconds.
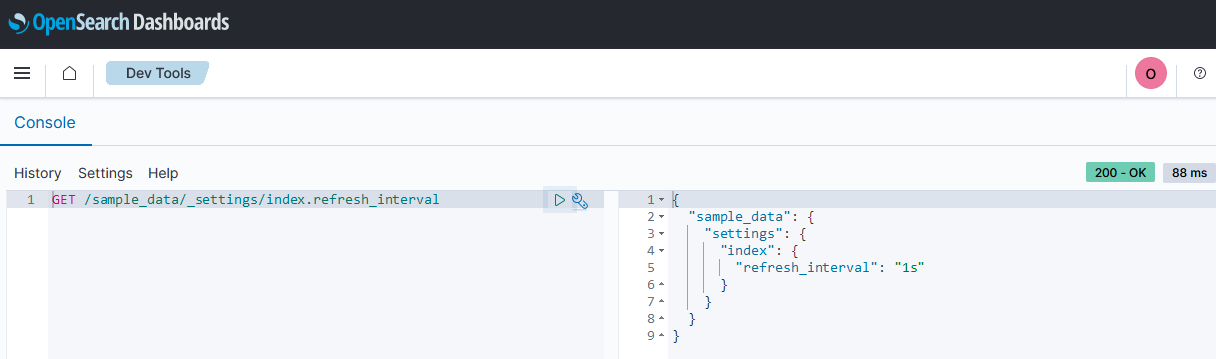
Assuming we are using an index named sample_data we can check what the refresh interval is for this index by running the following API command:
GET /sample_data/_settings/index.refresh_interval
In this example the refresh interval of the sample_data index is 1 second.
Note that if a refresh interval is not manually set, the API call may not return any results. The default refresh interval is 1 second, but this property is not automatically added to the _settings API response unless it is manually set or adjusted.
Change the refresh interval
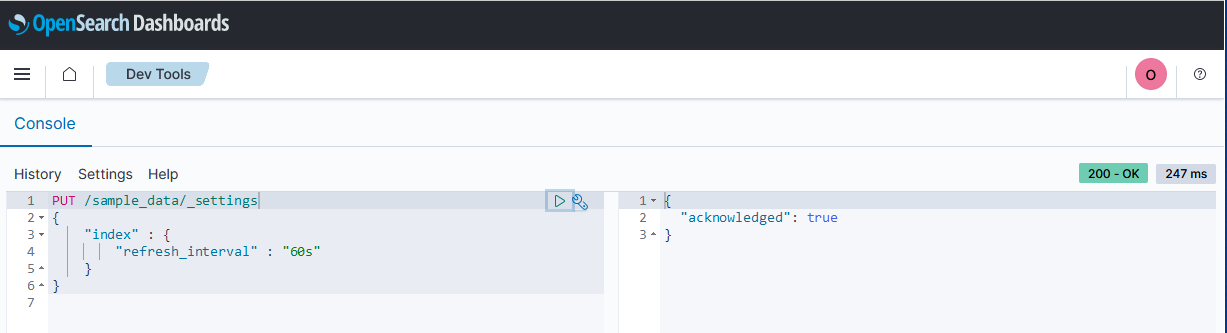
You can adjust the refresh interval for an index by using _settings API. In the following example, the refresh interval of the sample_data is set to 60 seconds:
PUT /sample_data/_settings
{
"index" : {
"refresh_interval" : "60s"
}
}
It is also possible to disable automatic refreshes. Setting "refresh_interval" : "-1" will disable any automatic refreshing. In this scenario, an index will need to be refreshed manually using the _settings API.
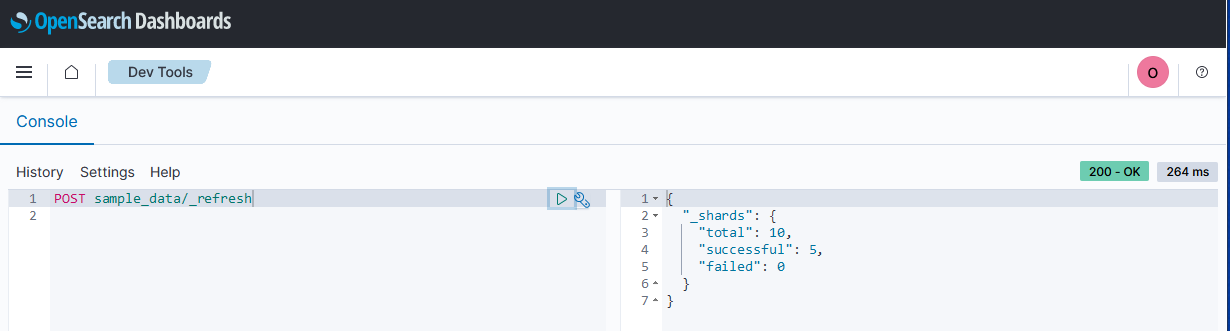
The following example API call manually triggers a refresh on the index sample_data:
POST sample_data/_refresh
You have the option to disable automatic refreshes prior to initiating a known write-intensive workload and then manually trigger a refresh upon its completion. For instance, if you’re uploading new data to OpenSearch daily through a batch process, it might be beneficial to disable automatic refreshes just before the batch process begins. After the process concludes, you can manually initiate a refresh.
Conclusion and other resources
Modifying the default refresh interval to strike a balance between the speed at which new documents become searchable and the CPU and I/O costs of the refresh operation can enhance OpenSearch performance. While a shorter refresh interval, which implies more frequent refreshes, allows documents to become searchable more rapidly post-indexing, it does so at the expense of increased resource utilization.
If you prefer to learn about this topic in the format of a video instead of a blog post, check out the YouTube video OpenSearch - How to change the refresh interval of an index. This blog post is based on the GitHub repository OpenSearch_Refresh_Interval.

